

Below are several data sets that will be used in a few basic statistical analyses. Please follow the directions and contact me if you have any questions. You will need Microsoft Excel 2003 or 2007 to perform the analyses.
If you chose to calculate them by hand, please refer to your STA 270 Basic Statistics textbook or any basic statistics text for the t-test formulas and df tables.
![]() Submit this assignment to the course facilitator as an
email message.
Submit this assignment to the course facilitator as an
email message.
Central Tendencies
Note: The mean, median and mode can be calculated using the descriptive statistics in the Data Analysis options. See below.
1. Mean
Formula: mean = sum of all scores / the number of scores.
Calculate the mean for the following data set.
Money spent by youth at a little league concession
| Youth | Amount Spent |
| 1 | $2.56 |
| 2 | $1.52 |
| 3 | $3.25 |
| 4 | $1.75 |
| 5 | $2.01 |
| 6 | $1.72 |
| 7 | $1.52 |
| 8 | $1.01 |
| 9 | $3.62 |
| 10 | $2.79 |
2. Median
The median is the point that divides a distribution of scores exactly in half. Remember, the median is a point in the distribution, it may or may not be an actual score.
Calculate the median using the same data set. First, arrange the scores from highest to lowest, then determine the median.
Scores
| $2.56 |
| $1.52 |
| $3.25 |
| $1.75 |
| $2.01 |
| $1.72 |
| $1.52 |
| $1.01 |
| $3.62 |
| $2.79 |
3. Mode
The mode is the most frequently occurring score - the score with the greatest frequency.
Calculate the mode using the previous data set.
![]()
Tests of Differences
4. t-Test
The t distribution tells you the probability that the difference you observe is due to chance is the null hypothesis is true. The t-test is a ratio of a statistic over a measure of variability.
Using the t distribution to test a hypothesis is very similar to using the normal distribution. The null hypothesis is that the two populations have the same mean, and thus any difference between the two sample means is due to chance.
The t distribution tells you the probability that the difference you observe is due to chance if the null hypothesis is true. You simply establish a Type 1 error level, and if your observed difference is less probable than the Type 1 error level, reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the two means came from populations with different means.
Calculate the t score for the following Independent-Samples t-test data set.
Self-esteem scores for a challenge course research study
| Experimental Group (X1) | Control Group (X2) |
| 74 | 39 |
| 89 | 51 |
| 48 | 88 |
| 57 | 79 |
| 62 | 59 |
| 71 | 69 |
| 40 | 43 |
From the Data Analysis Sheet, submit the following information:
|
4a. the df (degrees of freedom) | |
|
4b. the t Stat | |
|
4c. the t Critical o (one-tail test) | |
|
4d. depending on, if the t Stat is less than the t Critical o number, WOULD YOU REJECT THE NULL HYPOTHESIS? Yes or No |
![]() Submit this assignment to the course facilitator as an
email message.
Submit this assignment to the course facilitator as an
email message.
![]()
![]() Tips for working with
Microsoft Excel
Tips for working with
Microsoft Excel
NOTE: If the Data Analysis command is not on the Tools menu, you need to install the Analysis ToolPak in Microsoft Excel. This is an optional program in your existing Microsoft Excel 2007 software.
| Click the Microsoft Office button (located in the top left corner of the page), then click Excel Options | |
| Click Add-Ins, and then the Manage box, select Excel Add-ins. | |
| Click Go | |
| In the Add-ins available box, select the Analysis ToolPak check box,
then click OK (If you get prompted that the Analysis ToolPak is not currently installed on your computer, click Yes to install it. | |
| After you load the Analysis ToolPak , the Data Analysis command is avaialble in the Analysis group on the Data tab. |
![]()
1. Click on the Data tab,
2. Click on Data Analysis.
3. In the Analysis Tools box, select t-test paired Two Sample for Means
4. Select New Worksheet Ply
5. In the box that appears, for variable 1: drag a box around Column A; then drag a new box around Column B for variable 2; then
6. Click OK
7. This will calculate all the required answers.
![]()
![]() Formula
for calculating the Independent t-test (If you do not use Excel)
Formula
for calculating the Independent t-test (If you do not use Excel)
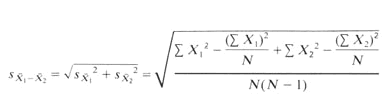 |
Key
![]() = Sum (add)
= Sum (add)
![]() = Scores
= Scores
![]() = Number of
scores
= Number of
scores
![]() = Standard
error of the mean for a sample
= Standard
error of the mean for a sample
![]() = Standard
error of the difference between means
= Standard
error of the difference between means
df (degrees of freedom) = N1 + N2 - 2
Reject the null if the t is 2.447 (at .05 Confidence Level) or lower.
![]()
![]() Copyright
2001. Northern Arizona University, ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
Copyright
2001. Northern Arizona University, ALL RIGHTS RESERVED